Even if you have a genetic predisposition to heart conditions, you can still reduce your risk by following the prevention strategies outlined in this article.
Your lifestyle plays a significant role in preventing heart disease. As one of the leading causes of death globally, heart disease is heavily influenced by the choices you make every day. This article will explore key strategies to help prevent heart disease.
Preventing Heart Disease: Key Strategies
Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps you can take to prevent heart disease. Smoking is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. It leads to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, causing atherosclerosis, and damages your organs, significantly increasing your risk of heart disease. Smoking reduces good cholesterol (HDL), raises blood pressure, and adds strain to your arteries.
Quitting smoking benefits are almost immediate—blood pressure drops, oxygen levels in tissues increase, and energy levels improve. Over time, your overall health will improve, and your risk of heart disease will decrease. Additionally, it’s important to avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can also contribute to heart disease.
Nutrition’s Role in Heart Disease Prevention
A healthy diet is crucial in reducing your risk of heart disease. Even if you are genetically predisposed to heart conditions, proper nutrition can help protect your heart. The Mediterranean diet, known for its heart health benefits, emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and healthy fats like olive oil. This diet includes:
- Abundant intake of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils such as olive oil.
- Limiting red meat consumption to once or twice a month.
- Increasing whole grain consumption.
- Including fatty fish in your diet twice a week.
Collagen and Heart Health
Collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, is vital for more than just maintaining youthful skin. It plays a crucial role in the health of bones, connective tissues, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. As we age, collagen levels naturally decline, which can contribute to heart disease. Collagen supports heart health in several ways:
- It helps maintain the strength and elasticity of arteries, preventing them from becoming weak or stiff.
- Adequate collagen levels can reduce bad cholesterol (LDL) in the blood, lowering the risk of plaque formation and artery narrowing, which in turn reduces heart attack risk.
- Collagen boosts nitric oxide levels in the body, which helps lower blood pressure and may aid in preventing heart disease.
Exercise and Weight Management for Heart Disease Prevention
Maintaining a healthy weight and incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine is essential for preventing heart disease and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. A 30-minute moderate-intensity workout is recommended for everyone. Staying active and burning calories helps maintain a normal body mass index (BMI) and reduces the risk of heart disease.

Managing Blood Pressure to Prevent Heart Disease
High blood pressure increases strain on the cardiovascular system, raising the risk of heart disease. To manage blood pressure effectively, consider the following:
- Follow a healthy, low-sodium diet.
- Engage in regular exercise.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid stress.
- Quit smoking.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Take blood pressure medications as prescribed by your doctor.
Stress Management
Managing stress is another crucial factor in preventing heart disease. Research has shown a strong link between chronic stress and the development of heart conditions. Stress can lead to poor sleep, headaches, and fatigue, all of which can overwork the heart and increase the risk of heart disease.
To manage stress effectively, consider practices such as yoga, deep breathing exercises, listening to calming music, spending time with close friends, and prioritizing good sleep hygiene.
Regular Heart Check-Ups and EKG Tests
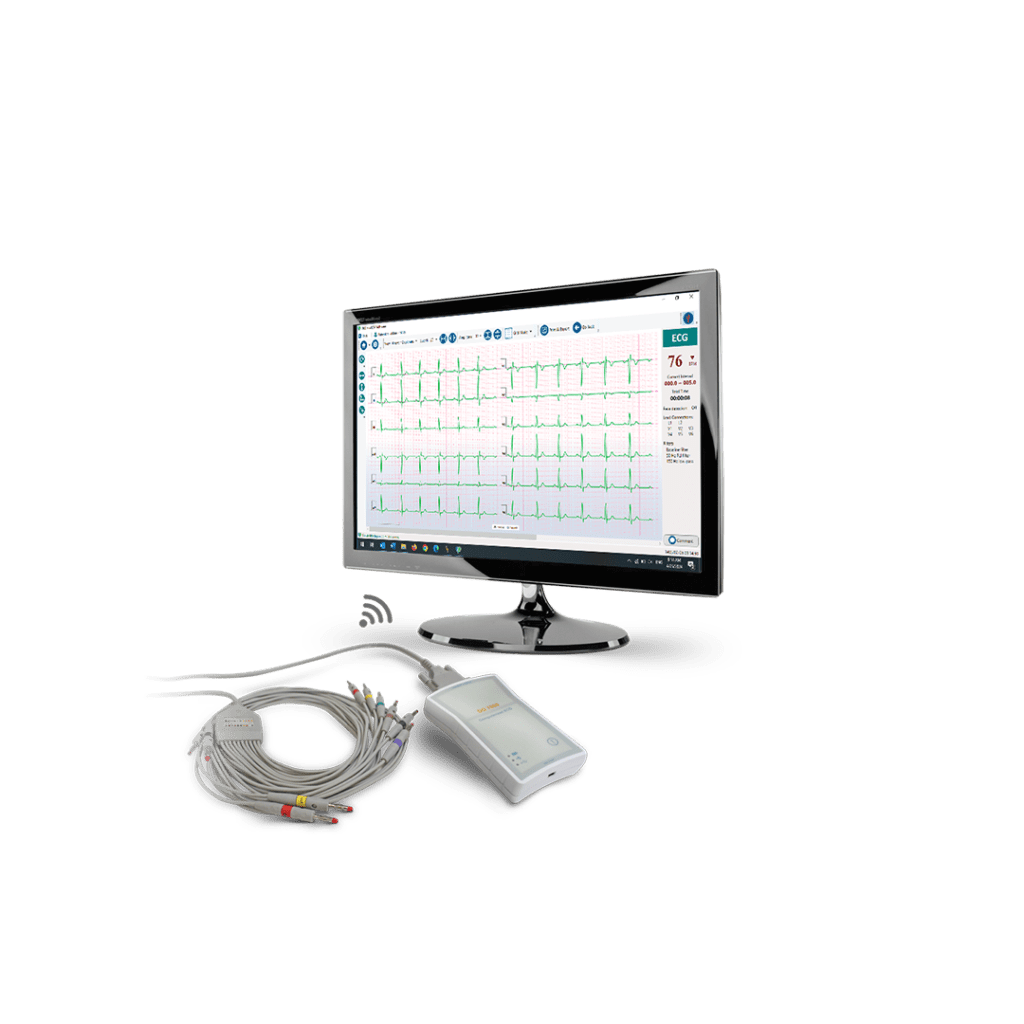
An electrocardiogram (EKG) is a simple, painless procedure that records the heart’s electrical activity. Small metal electrodes are placed on the wrists, ankles, and chest, transmitting electrical signals to the EKG machine, which displays these signals as waves. These waves represent the electrical activity in different areas of the heart.
The DG7000 is one of the most advanced electrocardiographs available today. This PC-based device connects to a computer to capture, record, process, and display a patient’s EKG. It is available in both WiFi and USB models, and its software is compatible with Windows operating systems.
Conclusion
To prevent heart disease, quit smoking, maintain a healthy diet, manage stress, keep your weight in a healthy range, reduce calorie intake if you are overweight, and regularly monitor your blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is the key to protecting yourself from heart disease and other serious health conditions. Doctors recommend that healthy individuals have their hearts checked by a specialist every 6 to 12 months.